Technical points for production of pollution-free vegetables
First, use high-efficiency and low-toxic pesticides It is strictly forbidden to use highly toxic and high-residue pesticides, such as 1605 , 007 Omethoate, Jiachao, etc. Instead, choose high-efficiency, low-toxic, and low-residue pesticides that are less harmful to natural enemies, such as carbendazim, chlorothalonil, brometholi Ester, mancozeb, and kelu. These options help maintain ecological balance while effectively managing pests. Second, the choice of production base The production base for pollution-free vegetables should be located away from industrial and mining pollution sources to avoid contamination from "three wastes." The environmental quality must comply with the standards outlined in DB221-946-2001 . This ensures a clean and safe environment for growing vegetables without harmful pollutants. Third, variety selection Selecting disease-resistant and insect-resistant varieties is crucial. For example, in protected areas, cucumber varieties like Qing 1 and Jin Chun series are ideal. Eggplant varieties such as Jijia No. 2 and black and bright are suitable, while pepper varieties like Fourth Pepper or tomato varieties like Kat Powder III and Good Powder 15 are also recommended. In open fields, Jizao No. 2 and Jiza No. 4 are good choices for cucumbers, and Jijiao No. 2 and Jijiao No. 3 for green peppers. Eggplants can benefit from Cigar No. 2 and Jijia No. 1. Fourth, pest control    1. Agricultural control: Before planting, remove all residual leaves, weeds, and diseased plant residues from the field and dispose of them through deep burial or burning. Avoid planting non-crop plants for more than three years to prevent soil degradation. Use techniques like black seed pumpkin grafting to reduce pest and disease risks.    2 , biological control: Utilize natural predators such as Lizard bees to manage greenhouse whiteflies. Apply biological pesticides like 2% brumamycin water at 200 times solution to treat cucumber anthracnose. Use 4% Chunleimycin wettable powder at 1000 times liquid to manage bacterial leaf spot. Apply 2.25 kg/ha of Bacillus thuringiensis wettable powder for foliar spray to control aphids and red spiders.    3. Physical control: Use yellow sticky traps and silver-gray strips to repel mites. Install insect-proof nets or shade nets to prevent pests. Implement high-temperature treatment at temperatures between 42 ~ 45 °C for 1.5 ~ 2 hours to prevent cucumber downy mildew. Soak seeds in warm water at 50 ~ 55 °C for 20 minutes for disinfection.    4. Chemical prevention and control: Conduct regular monitoring and forecasting of pests and diseases to act early. Apply appropriate chemicals timely, and alternate pesticide types to avoid resistance. Spray every 7 to 10 days, up to 3 to 4 times. Avoid using the same pesticide more than three times consecutively. Control fungal diseases with 72% dew, 69% manganese, and 75% chlorothalonil. For bacterial diseases, use 72% agricultural streptomycin sulfate or 30% DT wettable powder. For viral diseases, apply 20% virus A wettable powder. For pests, use 1.8% insect full emulsion, 1.8% pyroline wettable powder, or 2.5% deltamethrin EC. Fifth, formula fertilization Apply mature manure and pig manure mixed fertilizer, preferably biogas slag. The amount of fertilizer varies depending on the vegetable type and soil fertility. Limit chemical fertilizer usage and ensure proper application. Use potassium sulfate instead of potassium chloride. Apply ammonium-based nitrogen fertilizers, not nitrate nitrogen. For solanaceous crops, apply about 300 kg of diammonium phosphate and 50 kg of potassium sulfate. After flowering, apply fermented organic fertilizer once or twice during fruit development. In the production of pollution-free vegetables, reduce chemical fertilizer use and increase the application of biological fertilizers such as Tianda- 2216 , which improve soil health and enhance crop yield. Apply these fertilizers during the growth stage, and spraying once per fruiting period can boost yields by over 20% . Sixth, strictly control the safety interval of medication Different pesticides have different safety intervals. For instance, hydrogen bromide requires 3 days, chlorothalonil needs 7 days, carbendazim requires 25 days, and mancozeb needs 5 days. Ensure that pesticide residues do not exceed legal limits before harvesting. Harvest after the safety interval has passed, and use clean, hygienic tools to maintain product quality.  A comprehensive understanding and selection of different types of pH sensors are essential to improving the accuracy and reliability of pH measurements. Daruifuno's rich range of pH sensors is your best choice. Whether you are a scientist in a laboratory, a farmer managing soil conditions, or an engineer overseeing industrial processes, it is particularly important to understand and screen the types of pH sensors suitable for targeted specific industries. The following will delve into the details of each sensor type, including its principles, applications, and structural composition, to help you make an informed decision.  Principle: Digital pH sensors employ advanced digital signal processing techniques to convert pH measurements into digital data, ensuring high accuracy and reliability. Applications: These sensors are ideal for laboratory research, water quality analysis, and industrial processes where precision is paramount. They are also used in aquaculture and swimming pool maintenance. Structure: Composed of a pH-sensitive glass membrane, a reference electrode, and a digital output interface (such as USB or RS232), allowing seamless integration with data acquisition systems. Additional Details: Some models include temperature compensation to enhance accuracy across varying temperatures. Principle: Analog pH sensors operate by converting pH levels into proportional electrical signals, typically voltage or current, which can be measured using a multimeter or data logger. Applications: Widely used in environmental monitoring, agricultural soil testing, and basic laboratory experiments where cost-effectiveness and simplicity are key. Structure: Features a PH Electrode and a reference electrode, with analog output connections for interfacing with external devices. Often housed in a durable, waterproof casing. Additional Details: Calibration is typically required periodically to maintain accuracy, using standard buffer solutions.  Principle: Designed for continuous, real-time monitoring of pH levels in fluid systems, these sensors provide instant feedback on process conditions. Applications: Essential in wastewater treatment plants, chemical processing facilities, and food and beverage production lines where consistent pH control is critical. Structure: Incorporates a robust housing, self-cleaning mechanisms to prevent fouling, and digital communication protocols (e.g., Modbus, HART) for integration into process control systems. Additional Details: Many models include automatic temperature compensation and diagnostic features to alert operators to potential issues.  Principle: Transmits pH data as a 4-20mA current signal, which is less susceptible to electrical noise and can travel long distances without signal degradation. Applications: Commonly used in industrial automation, remote monitoring systems, and process control applications where reliable, long-distance communication is necessary. Structure: Consists of a pH electrode, signal conditioning circuitry to convert pH measurements into a 4-20mA signal, and a transmitter module for sending data to a central control system. Additional Details: These sensors often include features like loop-powered operation, which simplifies installation and reduces wiring complexity.  Principle: Specifically engineered to measure pH in nutrient solutions used in hydroponic systems, ensuring optimal plant growth conditions. Applications: Critical for maintaining the correct pH levels in hydroponic gardens, greenhouses, and vertical farming operations. Structure: Features a durable, water-resistant design with a pH-sensitive tip and a connection to monitoring devices or automated dosing systems. Additional Details: Some models are designed to be easily cleaned and calibrated, with replaceable tips to extend sensor life.  Daruifuno is committed to providing high-quality, reliable pH sensors of different types and models to meet the diverse needs of customers. Our sensors are designed with precision and durability in mind, ensuring accurate measurements and long-lasting performance. Whether you need a sensor for a small laboratory experiment or a large industrial process, we can provide you with the right solution.  Daruifuno's diverse range of types of pH sensors offers solutions tailored to various industries and applications. Whether you require high precision in a laboratory setting or continuous monitoring in an industrial environment, Daruifuno has a PH Sensor to meet your needs. Explore our offerings today and discover how we can help you unlock precision in PH Measurement . Types of pH Sensors,pH Sensors,pH Measurements Suzhou Delfino Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.daruifuno.comIntroduction
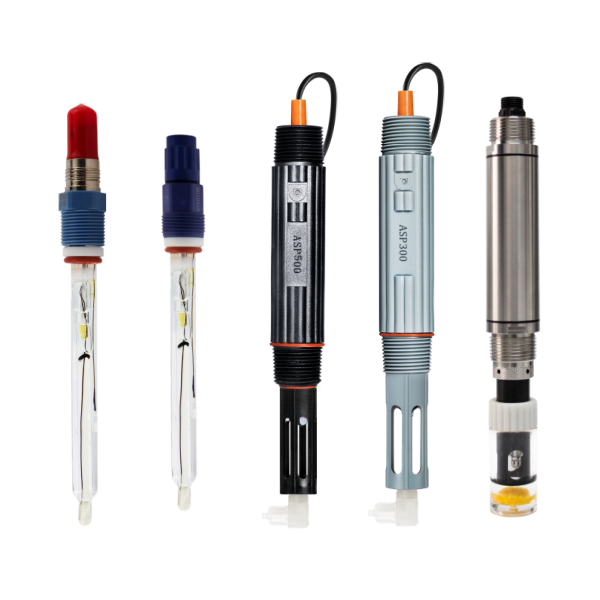
1. Digital PH Sensor
2. Analog PH Sensor
3. Online PH Sensor
4. 4-20mA PH Sensor
5. Hydroponics PH Probe
Why Choose Daruifuno?

Conclusion