How to understand the current exchange rate of RMB against the US dollar?
SLPC floor is a combination floor of lVT + SPC + LVT, which is a floor with special thickness newly produced by our company.
Schnell environmental protection flooring is more stable and with longer using life. It is suitable for ground heating system. We use the glass fiber layer to adjust the stability of the flooring. Schnell envirnmental protection flooring gives you the comfortable feeling experience and excellent thermal conductivity through temperature test. It has the advantages of freroof water-proof, moisture-proof, insect proof, stable structure, super wear-resistant. The special elastic structure of Schnell environmental protection flooring gives customers a more comfortable bare foot feeling, and gives new concept oflow-carbon environmental protection space with its characteristicsof environmental protection , comfort and fashion style.
6Mm Combination Floor,Slpc Flooring,6Mm Slpc Flooring,Waterproof Slpc Flooring Liaoning Schnell Interior Products Co., Ltd , https://www.schnellflooring.com
The current formation of the middle price includes three contents: market supply and demand, basket exchange rate and counter-cyclic factor, which respectively correspond to pinning with slope, random fluctuation, and correction of pinning slope. These three items are not new. As early as July 21, 2005, the announcement of the reform of the RMB exchange rate formation mechanism mentioned the market supply and demand as the basis, reference the basket currency, and maintain the basic stability of the RMB at a reasonable and balanced level. The central bank's guidance on exchange rate changes in the year is still a trade-off between these factors, but each factor has different specific indicators at different times, and the weights given are different.
The RMB exchange rate, which only considers the market supply and demand, has continued to depreciate in the past two years. The depreciation rate of each trading day is close. The exchange rate of the RMB against the US dollar is a pegged exchange rate with a slope. The current market supply and demand refers to (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day). Considering that the monetary authorities will buy or sell foreign exchange, the closing price will also be affected by the intervention of the foreign exchange market. Therefore, the closing price minus the middle price only partially reflects the market supply and demand. Figure 1 below shows the changes in the RMB exchange rate since the April 2016 (only the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day). From the morphological point of view, the exchange rate of the RMB against the US dollar is a pegged exchange rate with a slope.
Maintaining a relatively stable RMB-dollar exchange rate requires an unstable foreign exchange market intervention, and the foreign exchange market is under pressure to intervene. In the two years before 2017, the foreign exchange market was under great pressure, and the monetary authorities were forced to use foreign exchange reserves in large quantities. The size of China's foreign exchange reserves fell from 3.81 trillion US dollars at the beginning of 2015 to 3.01 trillion US dollars at the end of 2016. After entering 2017, the pressure on the foreign exchange market is in short supply. The foreign exchange market intervention required to maintain the gradual change of the exchange rate has fallen sharply, and the foreign exchange reserves have even rebounded slightly due to the valuation effect. 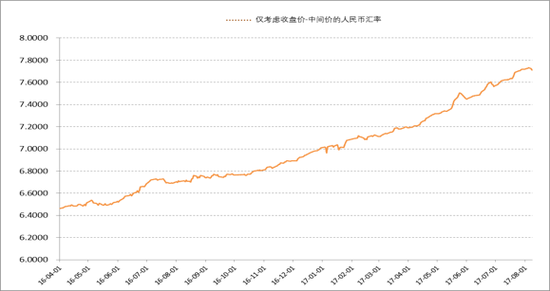
Figure 2 below shows the change in the exchange rate of RMB against the US dollar brought about by the stabilization of the basket exchange rate since April 2016. During this period, as the US dollar depreciated against the other currencies in the basket (April to December 2016) (January to August 2017), in order to maintain the exchange rate of the basket, the RMB should be depreciated against the US dollar and then appreciated. The US dollar among the basket currencies is a floating exchange rate system for other major currencies, such as the euro, the Japanese yen, the Australian dollar and the British pound. The exchange rate of the US dollar against these currencies fluctuates randomly, which makes it necessary to keep the exchange rate of the basket unchanged. fluctuation. The introduction of the basket exchange rate factor is essentially the introduction of random fluctuations in the exchange rate of the RMB against the US dollar. 
If the countercyclical coefficient is equal to -1, then (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) is completely offset, and does not affect the middle price of the next trading day. The slope of the exchange rate of the RMB against the US dollar caused by market supply and demand is zero. The renminbi exchange rate formation mechanism is morphologically fixed to the dollar and the exchange rate of the renminbi/dollar exchange required to maintain the exchange rate of the basket.
If this coefficient is equal to 0, then (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) and (the exchange rate change required to maintain the stability of the RMB against the basket currency) jointly determine the middle price of the next trading day, and the RMB exchange rate is formed. The mechanism is morphologically pegged to the US dollar with a slope, plus the change in the RMB/US dollar exchange rate needed to maintain the basket exchange rate unchanged.
If the coefficient is equal to between 0 and 1, the part (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) and (the exchange rate change required to maintain the stability of the RMB against the basket currency) jointly determine the next trading day. The middle price, the RMB exchange rate formation mechanism is morphologically pegged to the US dollar. The slope of the RMB exchange rate against the US dollar is lower than the slope when the countercyclical coefficient is equal to 0, plus the RMB caused by the basket exchange rate factor. / USD exchange rate changes.
Looking at the chart below, the impact of the closing price on the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day on the RMB exchange rate is weakening, which may be due to the introduction of the countercyclical adjustment factor. 
Observing the residual term of the above regression, the residual term has systematic downward deviation since 2017, and the part that cannot be explained by the model is more appreciation of the RMB against the US dollar. The reason for this may be that the influence coefficient on the middle price (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) has changed, that is, the countercyclical adjustment factor has been introduced. The impact on the middle price during the sample period (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) is the depreciation of the RMB against the US dollar. After the impact of this factor is discounted by the countercyclical factor, some RMB appreciation against the US dollar cannot be It is explained by a model that does not contain a countercyclical adjustment factor.
Using the data after May 2017 to make the above regression, the coefficients of the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day and the adjustment of the RMB/US dollar exchange rate required to maintain the basket exchange rate are 0.68 and 0.5 respectively. The two together explained a 75% change in the middle price. The regression coefficient (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) has dropped sharply from the previous sample period, from 0.96 to 0.68, which is visible (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) The impact on the middle price has been greatly reduced. After the countercyclical factor weakens (the closing price of the previous trading day - the middle price of the previous trading day) on the middle price, the impact of the basket exchange rate factor on the RMB/US dollar exchange rate is more prominent, given the weak dollar in recent months, The renminbi has appreciated significantly against the US dollar. Despite the recent improvement in the fundamentals of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market, the recent appreciation of the renminbi against the US dollar has come from the adjustment of the renminbi exchange rate pricing rules and cannot be explained by the fundamentals of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market.
Compared with the exchange rate formation mechanism that does not consider the countercyclical adjustment factor, the slope of the unilateral continuous depreciation of the RMB against the US dollar exchange rate declines. The exchange rate change is more dependent on the exchange rate changes of the US dollar against other currencies in the basket, while the latter changes are random changes. In this way, the unilateral devaluation/appreciation of the renminbi is expected to be intermittently mitigated, and the short-term capital flow pressure is also moderately mitigated.
The exchange rate of RMB against the US dollar under this mechanism may have more frequent fluctuations in form. The fluctuations mainly come from the exchange rate changes of the US dollar against other basket currencies; from the mechanism point of view, it is closer to the fixed exchange rate, because the exchange rate price changes more from the US dollar pair. Changes in the exchange rate of other currencies in the basket have only made a very limited response to the supply and demand of the domestic foreign exchange market.
Once important changes have taken place in domestic and international economic fundamentals, the required exchange rate adjustment pressure cannot be released under the current exchange rate mechanism. Exchange rate depreciation/appreciation expectations and capital outflow/inflow pressure will come back. It still requires a large amount of foreign exchange market intervention to maintain the target exchange rate. . Macroeconomic stability is still being kidnapped by exchange rate stability targets.